The Heart of Visual Computing: An Exploration of Graphics Cards
Graphics cards, also known as Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), are the unsung heroes of modern computing. From enabling breathtaking visuals in video games to accelerating data-intensive tasks like AI training and 3D rendering, these powerful components have revolutionized how we interact with technology. This essay delves into the significance of graphics cards, their components, applications, and the pivotal role they play in shaping our digital experiences.
Understanding Graphics Cards
At its core, a graphics card is a specialized piece of hardware designed to handle visual data. Unlike the Central Processing Unit (CPU), which executes general-purpose tasks, a GPU excels in parallel processing. This means it can handle multiple data streams simultaneously, making it indispensable for rendering complex images, animations, and other graphical tasks.
A graphics card typically comprises several key components:
GPU Chip: The brain of the graphics card, responsible for executing rendering tasks.
Video Memory (VRAM): Temporary storage for textures, shaders, and other visual data.
Cooling System: Prevents overheating and ensures stable performance during heavy workloads.
Connectors: Ports like HDMI, DisplayPort, and VGA allow the card to output visuals to monitors.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB): Houses the electronic components and connects them efficiently.
Applications of Graphics Cards
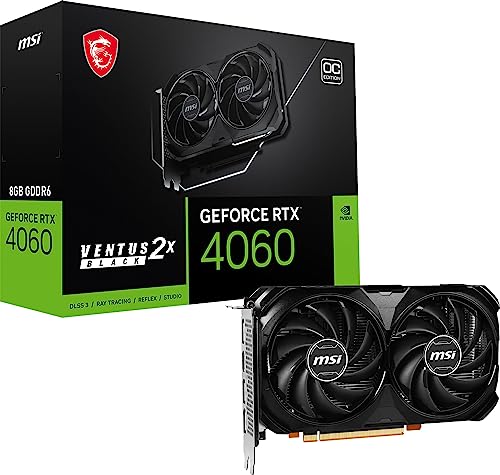
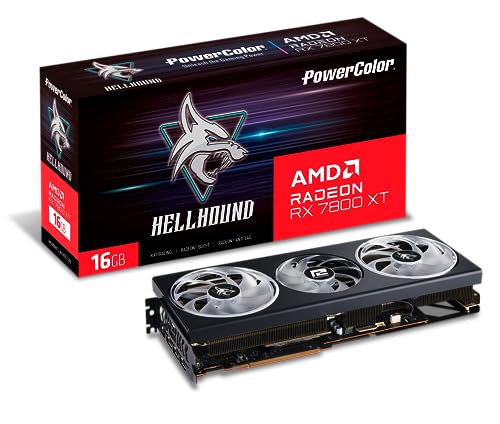
Gaming: Perhaps the most popular application of GPUs, gaming demands high frame rates, realistic textures, and advanced rendering techniques. High-end GPUs from NVIDIA (e.g., GeForce RTX) and AMD (e.g., Radeon RX) allow gamers to experience ultra-realistic visuals and smooth gameplay.
Content Creation: From video editing to 3D modeling, content creators rely heavily on GPUs. Software like Adobe Premiere Pro, Blender, and Autodesk Maya utilize GPU acceleration for faster rendering and improved productivity.
AI and Machine Learning: Graphics cards play a crucial role in artificial intelligence. GPUs’ ability to process vast amounts of data in parallel makes them ideal for training machine learning models and running AI algorithms.
Scientific Research: In fields like genomics, climate modeling, and astrophysics, GPUs are used to perform simulations and analyze massive datasets, significantly reducing processing time.
Cryptocurrency Mining: While controversial, GPUs are also employed in mining cryptocurrencies. Their parallel processing power is used to solve complex mathematical problems for blockchain validation.
Everyday Computing: Even for casual users, integrated GPUs or entry-level discrete cards improve video playback, browser performance, and multitasking capabilities.
Integrated vs. Dedicated Graphics Cards
Graphics cards can be broadly categorized into two types: integrated GPUs and dedicated GPUs. Integrated GPUs are built into the CPU, offering basic graphics performance suitable for everyday tasks like browsing, office work, and light gaming. Dedicated GPUs, on the other hand, are standalone components with their own VRAM and processing power. They deliver superior performance, making them essential for gaming, professional content creation, and other demanding applications.
The Evolution of Graphics Cards
The journey of graphics cards from simple 2D accelerators to the advanced GPUs of today is a testament to technological progress. The introduction of programmable shaders, real-time ray tracing, and AI-enhanced rendering has transformed the industry. Today, GPUs not only power personal computers but also fuel innovations in autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and cloud gaming.
Future of Graphics Cards
As technology continues to evolve, the future of GPUs looks brighter than ever. Innovations such as photorealistic ray tracing, quantum computing integration, and AI-powered optimizations are set to redefine their capabilities. Moreover, with the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, manufacturers are focusing on developing GPUs that deliver top-tier performance with reduced power consumption.
Conclusion Graphics cards are more than just tools for generating visuals—they are engines of progress, driving advancements across industries. Whether you’re a gamer exploring virtual worlds, a scientist solving complex problems, or an artist bringing visions to life, GPUs are central to your digital experience. As the world becomes more visually and computationally demanding, the role of graphics cards will only grow, continuing to shape the way we interact with technology and explore the possibilities of the digital frontier.
The Heart of Visual Computing: An Exploration of Graphics Cards
An Exploration of Graphics Cards
Related Articles
Top Picks for Best High Performance PCs
Find Your Perfect Powerhouse for Gaming and Work
Best High Performance PCs for Every Gamer
Find the perfect setup to boost your gaming experience
Best High Performance PCs You Can Buy Right Now
Unleash your gaming and productivity with top-notch computers available today
View our related products
See more